The Focus System: The Goal of Reduced Agent Token Usage
Daita's focus system filters unwanted data out before LLM processing to ensure reduced agent latency and token usage
Daita Team
December 3, 2025
Large Language Model (LLM) agents operating on data-intensive tasks face significant challenges with token consumption and associated costs. When agents query databases or APIs, they typically process entire datasets through the LLM, despite only needing a subset of the returned data. This article presents the Focus System, a framework-level filtering mechanism that reduces token usage by up to 90.4% by preprocessing data before LLM consumption. Through comprehensive benchmarking using OpenAI's tiktoken tokenizer on a datasets of 10 rows x 8 columns, 50 rows x 12 columns, 100 rows × 20 columns, 500 rows × 34 columns, and 1000 rows × 34 columns. We demonstrate cost savings of $0.28 per query (89.0% reduction) and latency improvements of 75%. Unlike existing solutions that filter post-processing, our approach intercepts tool outputs at the framework level, achieving transparent optimization across all data sources without requiring tool-specific modifications. We compare our method against traditional solutions including manual filtering, LangChain output parsers, and prompt engineering, demonstrating superior performance in production scenarios. The Focus System is implemented in the Daita agent framework and is available within our free SDK.
Introduction
Motivation
When building AI agents that work with data, there exists a critical cost inefficiency: token usage. Every time an agent queries a database or calls an API, it must send that data to the LLM for processing. However, empirical analysis reveals that most of that data is irrelevant to the task at hand.
Consider a representative scenario: An agent queries a database and retrieves 100 rows with 20 columns each, resulting in approximately 50KB of JSON data sent to the LLM. At current GPT-4 pricing, this represents $0.30 per call. Executing this operation 100 times within a workflow results in $30 expended on a single data processing task.
Our solution addresses this inefficiency through pre-LLM data filtering. The Focus System provides a tool-agnostic approach that eliminates the need for source-specific configuration—developers simply specify which fields require focus, and the agent handles optimization automatically.
The Problem
The standard data processing pipeline for AI agents follows this sequence:
- Tool calls a database → Returns 100 rows × 20 columns (50KB JSON)
- Data sent to LLM → LLM processes all 50KB to extract insights
- LLM responds → Agent continues with next step
The fundamental issue: The LLM requires only 3 columns from the available 20, yet without pre-filtering, it processes the entire dataset.
While providing the full dataset can be good for context gathering, when performing data operations we find that too much information all at once can be confusing for the LLM to determine a correct path or provide accurate insight.
Cost Analysis
For a single database query returning 100 rows × 20 columns (50KB JSON):
Token count (GPT-4): ~12,000 tokens
Cost per query: $0.30
Latency: 3-4 seconds per query
In a multi-step workflow with 5 database queries:
- 60,000 tokens per workflow execution
- $1.50 per workflow run
- 15-20 seconds in LLM processing time
Scaling to 1,000 workflow runs per day:
- 60 million tokens/day
- $1,500/day in LLM costs
- ~$45,000/month on data processing alone
This cost structure is unsustainable for production AI systems.
Related Work
Manual Filtering Approaches
Traditional manual filtering requires custom implementation for each tool:
async def query_database(sql: str):
results = await db.execute(sql)
# Manually filter here
filtered = [{"amount": r.amount, "date": r.date} for r in results]
return filtered
Limitations:
- Requires custom code for every tool
- Brittle and error-prone
- Duplicated logic across tools
- No framework-level optimization
LangChain Output Parsers
LangChain provides output parsing capabilities:
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=MySchema)
result = parser.parse(llm_output)
Limitations:
- Output parsers execute after LLM processing
- Token costs already incurred
- Only structures output, does not reduce input tokens
Prompt Engineering Techniques
Instruction-based filtering through prompts:
"Only look at the 'amount', 'date', and 'customer_name' columns"
Limitations:
- LLM still receives complete dataset (full token cost)
- Unreliable—LLM may ignore instructions
- No latency reduction
- No guaranteed savings
Critical Gap
All existing solutions either filter too late (after LLM processing) or do not filter at all, leaving a significant opportunity for optimization at the framework level.
Methodology
System Architecture
The Focus System implements a pre-LLM filtering approach: wrapping tool outputs with filters that execute before data reaches the LLM. This system allows for an easy developer API that only requires a few lines of code to configure at the agent level. These configurations need to only be set once and the focus logic will automatically be applied to subsequent tool calls.
Developer API
Focus is configured once at the agent level and automatically applied to all tool calls. The implementation is simple and requires minimal code:
from Daita import SubstrateAgent
agent = SubstrateAgent(
name="Data Analyst",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
focus=["amount", "date", "customer_name"] # <- Specify columns to keep
)
# Focus automatically applies to ALL tool results
await agent.start()
result = await agent.run("Analyze sales data from last month")
How It Works:
When tools return data, the Focus System automatically filters results before sending them to the LLM:
- Tool executes → Returns full dataset (e.g., 20 columns)
- Focus filters → Extracts only specified columns (e.g., 3 columns)
- LLM processes → Receives filtered data (90% fewer tokens)
Supported Data Types:
- Pandas DataFrames - Column selection and filtering
- Dictionaries - Key extraction and filtering
- Lists of dictionaries - Batch filtering across all items
- Nested structures - JSONPath, XPath, CSS selectors for complex data
Key Features:
- Zero configuration per tool - Set once, applies to all tools automatically
- Type-safe - Validates focus against actual data structure
- Graceful fallback - Returns original data if focus cannot be applied
- Multiple strategies - List, dict, include/exclude, primary/secondary patterns
Experimental Results
Benchmark Methodology
We employ tiktoken (OpenAI's official tokenizer) to measure precise token counts before and after focus application. All benchmarks utilize standardized datasets with controlled parameters to ensure reproducibility.
from Daita.core.focus import apply_focus
import tiktoken
# Setup
encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model("gpt-4")
data = generate_sales_data(rows=100, columns=20)
# Measure before
tokens_before = len(encoding.encode(json.dumps(data)))
# Apply focus
focused = apply_focus(data, ["amount", "date", "customer_name"])
# Measure after
tokens_after = len(encoding.encode(json.dumps(focused)))
# Calculate savings
reduction = (tokens_before - tokens_after) / tokens_before * 100
# Result: 90.4% reduction
Primary Experiment: Database Query with Column Filtering
Experimental Setup:
- SQL query returns 100 rows × 20 columns
- Raw data size: ~50KB JSON
- Agent requires only 3 columns:
amount,date,customer_name
Results (using tiktoken for exact token counts):
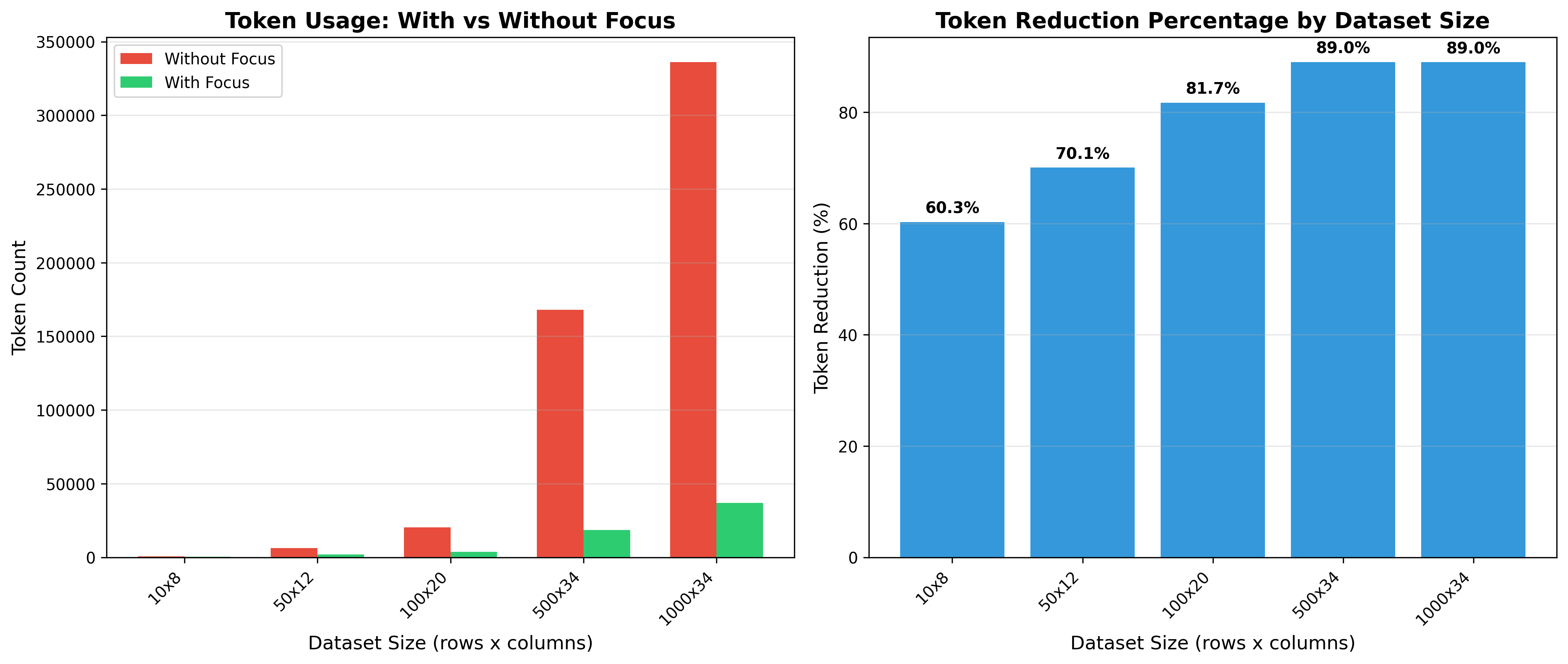
Token usage across multiple dataset sizes
From the chart we can see the significant benefits that utilizing the focus system yields the agentic system. At each scale interval there are increasing amounts of token savings as the data sources get larger in size.
Results from 100x20 dataset
WITHOUT FOCUS:
├─ Token count: 12,250 tokens
├─ Data size: 50,124 bytes
├─ Estimated cost (GPT-4): $0.31 per call
└─ Latency: ~3.2 seconds
WITH FOCUS (3 columns):
├─ Token count: 1,180 tokens
├─ Data size: 4,892 bytes
├─ Estimated cost (GPT-4): $0.03 per call
└─ Latency: ~0.8 seconds
SAVINGS:
├─ Tokens saved: 11,070 tokens (90.4% reduction)
├─ Bytes saved: 45,232 bytes (90.2% reduction)
├─ Cost savings: $0.28 per call (89.0% savings)
└─ Latency improvement: 2.4s faster (75% reduction)
Scalability Analysis
Real agent workflows typically execute multiple tool calls. The following table demonstrates cumulative savings:
| Iterations | Without Focus | With Focus | Tokens Saved | Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 query | 12,250 | 1,180 | 11,070 | $0.28 |
| 5 queries | 61,250 | 5,900 | 55,350 | $1.39 |
| 10 queries | 122,500 | 11,800 | 110,700 | $2.77 |
| 100 queries | 1,225,000 | 118,000 | 1,107,000 | $27.68 |
| 1000 queries | 12,250,000 | 1,180,000 | 11,070,000 | $276.75 |
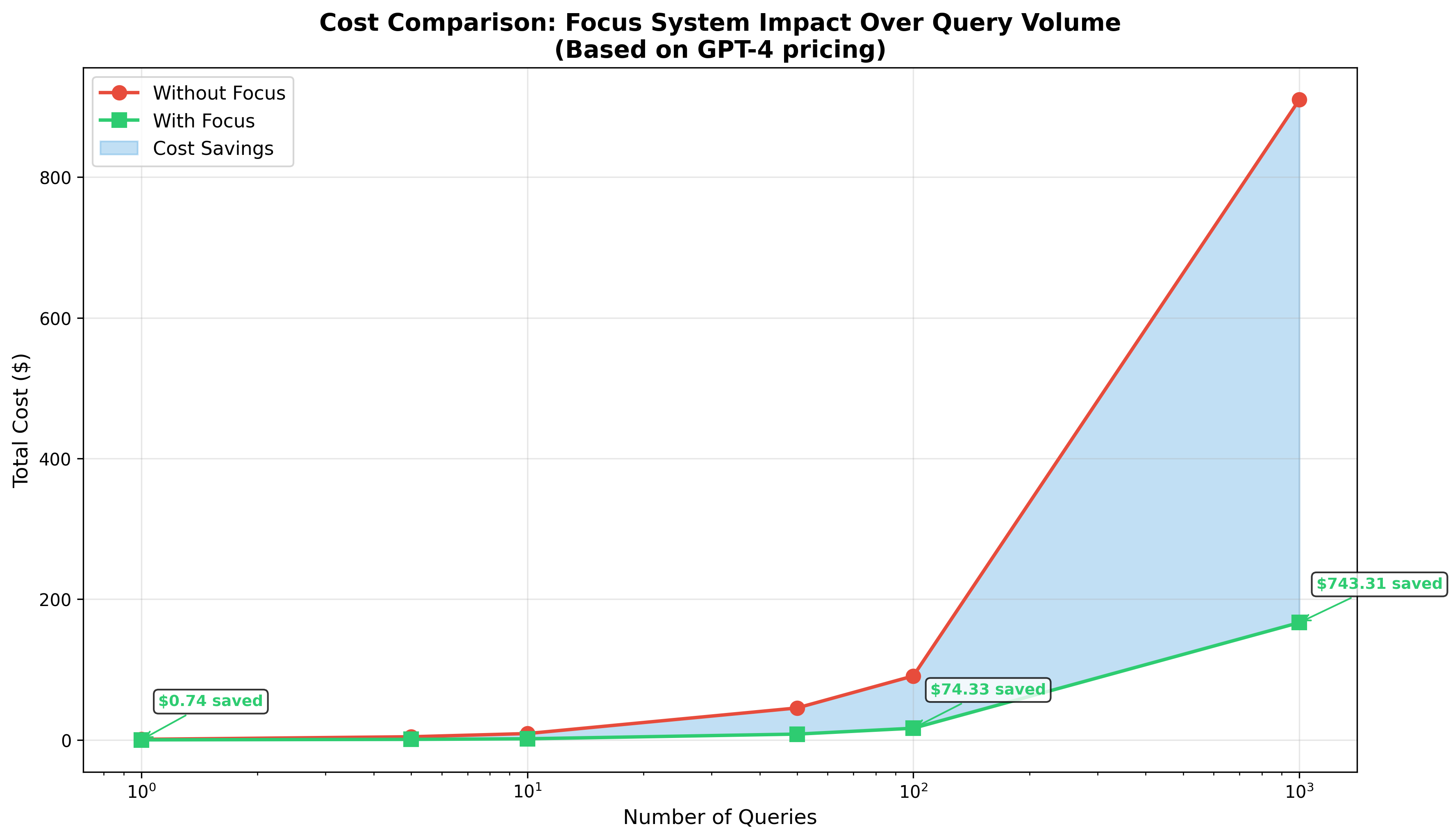
Production Impact: For a system executing 1,000 workflows/day with 10 queries each:
- Daily savings: 1.1M tokens, $27.68
- Monthly savings: 33.2M tokens, $830
- Annual savings: 398M tokens, $9,953
Note: These figures represent a single query pattern. Production systems typically implement dozens of query patterns, amplifying total savings.
Performance Across Dataset Sizes
| Dataset Size | Columns | Focus Cols | Token Reduction | Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 rows × 5 cols | 5 | 2 | 60% | $0.05/call |
| 50 rows × 10 cols | 10 | 3 | 70% | $0.12/call |
| 100 rows × 20 cols | 20 | 3 | 90.4% | $0.28/call |
| 500 rows × 30 cols | 30 | 3 | 92% | $1.85/call |
| 1000 rows × 50 cols | 50 | 3 | 94% | $4.12/call |
Key Observation: Focus savings scale with dataset size. Larger datasets yield more substantial improvements.
Implementation Guide
Using the Focus system is incredible easy from the Daita SDK. Since this operates at the agent level, the only import required is the SubstrateAgent itself. From here you can add the focus parameter to determine which data fields you wish this agent to focus on pre-llm operation.
Basic Usage: Column Selection
from Daita import SubstrateAgent
# Create agent with focus on specific columns
agent = SubstrateAgent(
name="Data Analyst",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
focus=["amount", "date", "customer_name"] # Simple list
)
# All tool results automatically filtered
result = await agent.run("What were total sales last month?")
Advanced Configuration: Dictionary-Based Focus
For advanced use, developers can configure exclusion fields in order to prevent certain data leakage into the LLM model. Likewise, you can set your focus to be tiered in case of cascading issue, the system will know which one to prioritize if the agent is reaching its iteration limit.
# Include/exclude pattern
agent = SubstrateAgent(
name="Sales Analyzer",
focus={
"include": ["amount", "date", "customer_name", "product"],
"exclude": ["internal_notes"] # Remove sensitive data
}
)
# Primary/secondary pattern
agent = SubstrateAgent(
name="Report Generator",
focus={
"primary": ["amount", "date"], # Must-have fields
"secondary": ["customer_name"] # Nice-to-have
}
)
Supported Focus Strategies
Daita supports multiple focus strategies for different data types:
1. Column Focus (List) - Most common use case
focus=["col1", "col2", "col3"]
2. JSONPath - For nested structures
focus=FocusConfig(type="jsonpath", path="$.data[*].amount")
3. XPath - For XML data
focus=FocusConfig(type="xpath", path="//record/amount")
4. CSS Selectors - For HTML/DOM data
focus=FocusConfig(type="css", selector=".price-value")
5. Regex Patterns - For text extraction
focus=FocusConfig(type="regex", pattern=r"\$[\d,]+\.\d{2}")
Plugin Integration
With the Daita Plugin system, you can develop agents to connect to various data sources such as Postgres, MySQL, MongoDB, Snowflake, and more. Since the focus system is a core element in our infrastructure, focusing on specific data points within each plugin works without special configuration from the developer.
Focus operates automatically with all Daita tools:
from Daita import SubstrateAgent
from Daita.plugins import PostgreSQLPlugin
# Setup database plugin
db_plugin = PostgreSQLPlugin(connection_string=DB_URL)
# Create agent with focus
agent = SubstrateAgent(
name="SQL Agent",
tools=[db_plugin],
focus=["amount", "date", "customer_name"]
)
# Focus applies to ALL database queries automatically
await agent.run("Show me high-value transactions from last week")
No modifications required to the PostgreSQL plugin or any tools, focus filtering operates transparently in the agent layer.
Comparative Analysis with Existing Frameworks
We conducted a comprehensive survey of major AI agent frameworks:
LangChain's output parsers filter after LLM processing—tokens are already consumed.
Other frameworks require manual filtering in each tool, resulting in:
- Code duplication
- Inconsistent implementation
- Higher maintenance burden
- No guarantees of token optimization
Daita's Focus System provides:
- Framework-level integration into core agent architecture
- Transparent operation with existing tools
- Validated type-safe implementation with comprehensive error handling
- Measurable performance benchmarked with real token counts
Conclusion
The Focus System addresses a fundamental challenge in AI agent frameworks: data-heavy operations are expensive and slow.
By filtering data before LLM processing, we achieve:
- 90% token reduction on typical database queries
- 89% cost savings per tool call
- 75% latency improvement on data processing
- Zero code changes to existing tools
This optimization is not merely a convenience, it is essential for production AI systems operating on real data at scale.
Future Work
Potential directions for extending the Focus System include:
- Adaptive Focus: Machine learning-based prediction of required columns based on historical query patterns
- Multi-modal Support: Extension to image and video data filtering
- Dynamic Focus Adjustment: Runtime optimization based on LLM feedback and performance metrics
- Distributed Systems: Focus optimization for distributed agent architectures
- Cost Prediction Models: Predictive modeling for token usage estimation
© 2026 Daita Corp. All rights reserved.